Find a Physician
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
Clinical Services
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
- About Single Ventricle Defects
- Arrhythmia Management and Electrophysiology Services
- Cardiac Surgery
- Cardiology
- Cardiopulmonary Exercise Laboratory
- Cardiovascular Genetics Research
- Catheterization Laboratory Research
- Congenital Heart Center Outcomes
- Contact Us
- Developmental Biology Research
- Electrophysiology Research
- Fellowship Program
- Fetal Cardiology Research
- Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation Research
- Interstage Surveillance Program
- In the News
- Make an Appointment
- Meet Our Team
- Non-Invasive Imaging Laboratory
- Non-Invasive Imaging Laboratory Research
- Our Compassionate Approach
- Our History of Leadership
- Our Patient Volume and Experience
- Our Research Commitment
- Our Specialized Programs
- Outcomes
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
- Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Laboratory Research
- Pediatric Heart Network Research
- Preventive Cardiology Program
- Pulmonary Hypertension Comprehensive Care Center
- Pulmonary Hypertension Research
- Resources for Parents
- The Center for Single Ventricle Care
- What to Expect
- Why Choose Us
- Why Choose Us for Your Child's Care
- Your Child's Healthcare Team
Health Information
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
Research and Clinical Trials
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
For Patients, Families & Visitors
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
Professionals
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
Hospital News
Return to About the Heart and Blood Vessels Overview
More on About the Heart and Blood Vessels
About the Heart and Blood Vessels
About the Heart and Blood Vessels
The heart is the hardest working muscle in the human body. Located almost in the center of the chest, the heart of a child is about the size of his/her fist. During an average lifetime, the human heart will beat more than three billion times - pumping an amount of blood that equals about one million barrels. The heart is always working, 24 hours a day, seven days a week - even while we are sleeping.
A child's heart works just as hard as an adult's heart. In fact, a baby' s heart may beat up to 190 times a minute, while an adult's heart usually beats between 60 and 100 times a minute. The rate at which the heart pumps gradually slows down from birth to adolescence.
Composed of the heart and blood vessels, the cardiovascular system is responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. A healthy cardiovascular system is vital to supplying the body with oxygen and nutrients.
How the heart works:
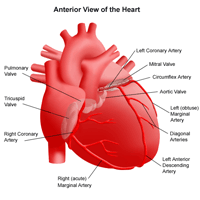
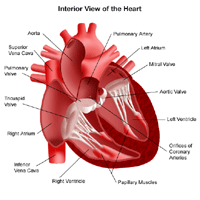
The heart is a large, hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood filled with oxygen and nutrients through the blood vessels to the body tissues. It is made up of:
- four chambers (two atria and two ventricles) that receive blood from the body and pump out blood to it.
- The right and left atria receive blood coming back to the heart.
- The right and left ventricles pump the blood out of the heart.
- four valves to prevent backward flow of blood: the aortic, pulmonary, mitral, and tricuspid valves. Each valve is designed to allow the forward flow of blood and prevent the backward flow.
- blood vessels that bring blood to the lungs, where oxygen enters the bloodstream, and then to the body.
- The inferior and superior vena cava bring oxygen-poor (blue) blood from the body into the right atrium.
- The pulmonary artery channels oxygen-poor (blue) blood from the right ventricle into the lungs, where oxygen enters the bloodstream.
- The pulmonary veins bring oxygen-rich (red) blood to the left atrium.
- The aorta channels oxygen-rich (red) blood to the body.
- An electrical system stimulates contraction of the heart muscle.
A network of arteries and veins also carry blood throughout the body.
- Arteries transport blood from the heart to the body tissues.
- Veins carry blood back to the heart.
Click here to view the
Online Resources of Cardiovascular Disorders